1. Leukemiahttps://apnacare.me/?p=405
Leukemia originates in the blood and bone marrow, leading to the production of abnormal white blood cells. These abnormal cells interfere with the bone marrow’s ability to produce healthy blood cells2. Types of leukemia include BLOOD CANCER.
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL): Common in children.
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML): More common in adults.
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): Typically affects adults over 55.
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML): Usually affects adults.
2. Lymphoma
Lymphoma affects the lymphatic system, which is part of the immune system. It involves the production of abnormal lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell)2. Types of lymphoma.
- Hodgkin Lymphoma: Characterized by the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells.
- Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: Includes various subtypes like follicular lymphoma and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
3. Myeloma
Myeloma affects plasma cells, which are white blood cells that produce antibodies. Multiple myeloma is the most common type and can cause bone pain, kidney problems, and weakened immune function2.
Symptoms of Blood Cancer
Common symptoms include:
- Persistent Fatigue and Weakness
- Fever and Chills
- Unexplained Weight Loss
- Night Sweats
- Bone and Joint Pain
- Frequent Infections
- Swollen Lymph Nodes
Symptoms of Blood Cancer
Diagnosis typically involves blood tests, bone marrow biopsy, and imaging studies. Treatment options vary based on the type and stage of cancer and may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and stem cell transplant.
1.Persistent Fatigue and Weakness
Common Causes
- Lack of Sleep: Not getting enough high-quality sleep can lead to chronic fatigue. Aim for at least 7-8 hours of sleep per night1.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Deficiencies in iron, vitamin B12, vitamin D, and other essential nutrients can cause fatigue. Consider getting your nutrient levels checked and discuss supplementation with your healthcare provider if needed1.
- Stress: Chronic stress can lead to physical and mental exhaustion. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or yoga.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like anemia, thyroid disorders, diabetes, and chronic fatigue syndrome can cause persistent fatigue. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Dehydration: Not drinking enough water can lead to fatigue and weakness. Make sure to stay hydrated throughout the day.
- Poor Diet: A diet high in processed foods and low in nutrients can contribute to fatigue. Focus on a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can lead to decreased energy levels. Incorporate regular exercise into your routine to boost your energy.
Tips to Address Fatigue and Weakness
- Prioritize Sleep: Establish a regular sleep schedule and create a relaxing bedtime routine.
- Eat Nutrient-Rich Foods: Include a variety of nutrient-dense foods in your diet to ensure you’re getting all the necessary vitamins and minerals.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to maintain hydration.
- Manage Stress: Practice relaxation techniques and consider seeking support from a therapist if needed.
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in physical activity to improve energy levels and overall well-being.
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: If fatigue persists, it’s important to seek medical advice to rule out any underlying health conditions.
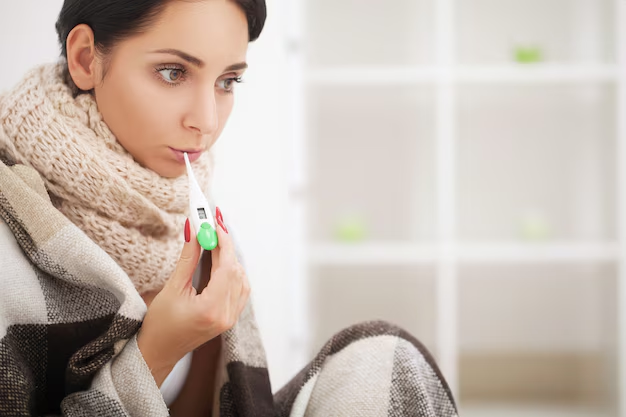
2.Fever and Chills
Common Causes
- Infections: Viral infections like the flu, common cold, and COVID-19, as well as bacterial infections like pneumonia and urinary tract infections (UTIs), can cause fever and chills2.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and Crohn’s disease can lead to fever and chills.
- Medications: Some medications, including antibiotics and antiseizure drugs, can cause fever as a side effect.
- Other Illnesses: Conditions like appendicitis, gastroenteritis, and even certain cancers can cause fever and chills.
Tips for Managing Fever and Chills
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration.
- Rest: Ensure you get plenty of rest to help your body fight off the infection.
- Medications: Over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil) can help reduce fever and alleviate discomfort.
- Cool Compress: Apply a cool, damp cloth to your forehead or take a lukewarm bath to help lower your body temperature.
- Monitor Symptoms: Keep track of your symptoms and seek medical attention if your fever is very high, persistent, or accompanied by severe symptoms like difficulty breathing, confusion, or a stiff neck

3.Unexplained Weight Loss
Common Causes
- Medical Conditions:
- Hyperthyroidism: An overactive thyroid can cause rapid weight loss.
- Diabetes: Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to weight loss.
- Cancer: Certain cancers can cause significant weight loss.
- Infections: Chronic infections like tuberculosis or HIV can lead to weight loss.
- Digestive Disorders: Conditions like Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, and ulcerative colitis can cause weight loss due to malabsorption and decreased appetite.
- Chronic Inflammation: Diseases like rheumatoid arthritis can increase metabolism and lead to weight loss.
- Mental Health Conditions:
- Depression and Anxiety: These conditions can affect appetite and lead to unintentional weight loss.
- Medications:
- Side Effects: Some medications can cause weight loss as a side effect.
Steps to Take
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: If you experience unexplained weight loss, it’s important to seek medical advice to determine the underlying cause.
- Keep a Food Diary: Track your food intake and any changes in appetite or eating habits.
- Monitor Other Symptoms: Note any additional symptoms such as fatigue, fever, or pain, and share them with your doctor.
- Follow Up: Regular follow-up appointments can help monitor your progress and adjust treatment plans as needed.
4.Night Sweats
Common Causes
- Menopause: Hormonal fluctuations during menopause are a common cause of night sweats in women.
- Infections: Conditions like tuberculosis and HIV can cause night sweats.
- Medications: Some medications, including antidepressants and medications for diabetes, can cause night sweats as a side effect.
- Hormonal Issues: Conditions like hyperthyroidism and low testosterone levels can lead to night sweats3.
- Cancers: Certain cancers, such as lymphoma and leukemia, can cause night sweats.
- Sleep Disorders: Conditions like obstructive sleep apnea can lead to night sweats.
- Stress and Anxiety: Mental health issues can also contribute to night sweats.
Tips for Managing Night Sweats
- Keep Your Bedroom Cool: Maintain a cool room temperature and use fans or air conditioning.
- Choose Breathable Bedding: Use moisture-wicking fabrics like cotton or bamboo for your sheets and pajamas.
- Avoid Triggers: Limit alcohol, caffeine, and spicy foods before bedtime.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated.
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: If night sweats persist, it’s important to seek medical advice to rule out any underlying health conditions.
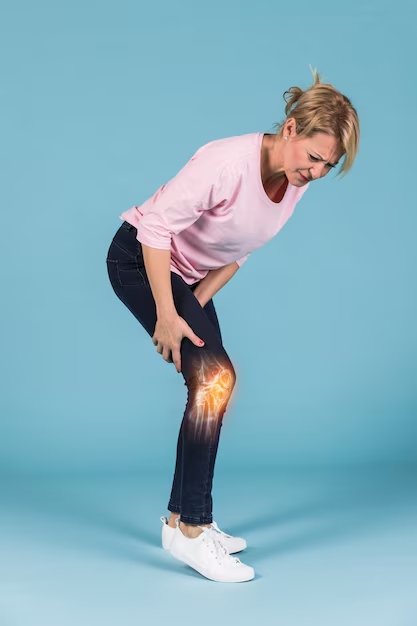
5.Bone and Joint Pain
Common Causes
- Arthritis: Inflammation of the joints, which can cause pain, stiffness, and swelling. Types include osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis1.
- Injuries: Trauma from accidents, sports, or falls can lead to bone fractures, sprains, and strains.
- Infections: Conditions like osteomyelitis (bone infection) and septic arthritis (joint infection) can cause pain.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Diseases like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis can cause joint pain.
- Gout: A form of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints, often affecting the big toe.
- Osteoporosis: A condition where bones become weak and brittle, leading to pain and fractures.
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of the tendons, which can cause pain around the joints.
- Fibromyalgia: A chronic condition characterized by widespread pain, including in the bones and joints.
Tips for Managing Bone and Joint Pain
- Rest: Give your body time to heal by avoiding activities that cause pain.
- Ice and Heat Therapy: Apply ice packs to reduce inflammation and heat packs to relax muscles and improve blood flow.
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises and stretches can improve strength and flexibility, reducing pain.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can put extra stress on your joints, so maintaining a healthy weight can help alleviate pain.
- Stay Active: Gentle exercises like walking, swimming, or yoga can help keep your joints flexible and strong.
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: If the pain persists or worsens, it’s important to seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment.

6.Frequent Infections
Common Causes
- Weakened Immune System: Conditions like HIV/AIDS, diabetes, and certain cancers can weaken your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections.
- Chronic Stress: Prolonged stress can suppress your immune system, increasing your risk of infections.
- Poor Nutrition: A diet lacking essential nutrients can impair your immune function.
- Lack of Sleep: Not getting enough quality sleep can weaken your immune system.
- Smoking and Alcohol: Both can impair your immune system and increase your risk of infections.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to pollutants, allergens, and other irritants can make you more prone to infections.
- Medical Treatments: Certain treatments like chemotherapy can weaken your immune system.
Tips for Reducing Infections
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to support your immune system.
- Get Enough Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to help your body fight off infections.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to keep your body hydrated and support immune function.
- Manage Stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol: Quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption to help maintain a strong immune system.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash your hands frequently, especially before eating or touching your face, to reduce the spread of germs.
- Stay Up-to-Date with Vaccinations: Ensure you’re up-to-date with recommended vaccinations to protect against infections.
